Since your vehicle cannot talk, it uses codes, messages, chimes, and symbols to communicate to you. Whenever an engine code appears, the vehicle’s Electronic Control Unit (ECU) has detected a problem with your engine. However, you should not panic when this code appears because it does not always mean that you have a major engine problem on your hands. Sometimes the engine issues that trigger this code are minor and easy to fix.
Different Engine Code Meanings and Troubleshooting Tips
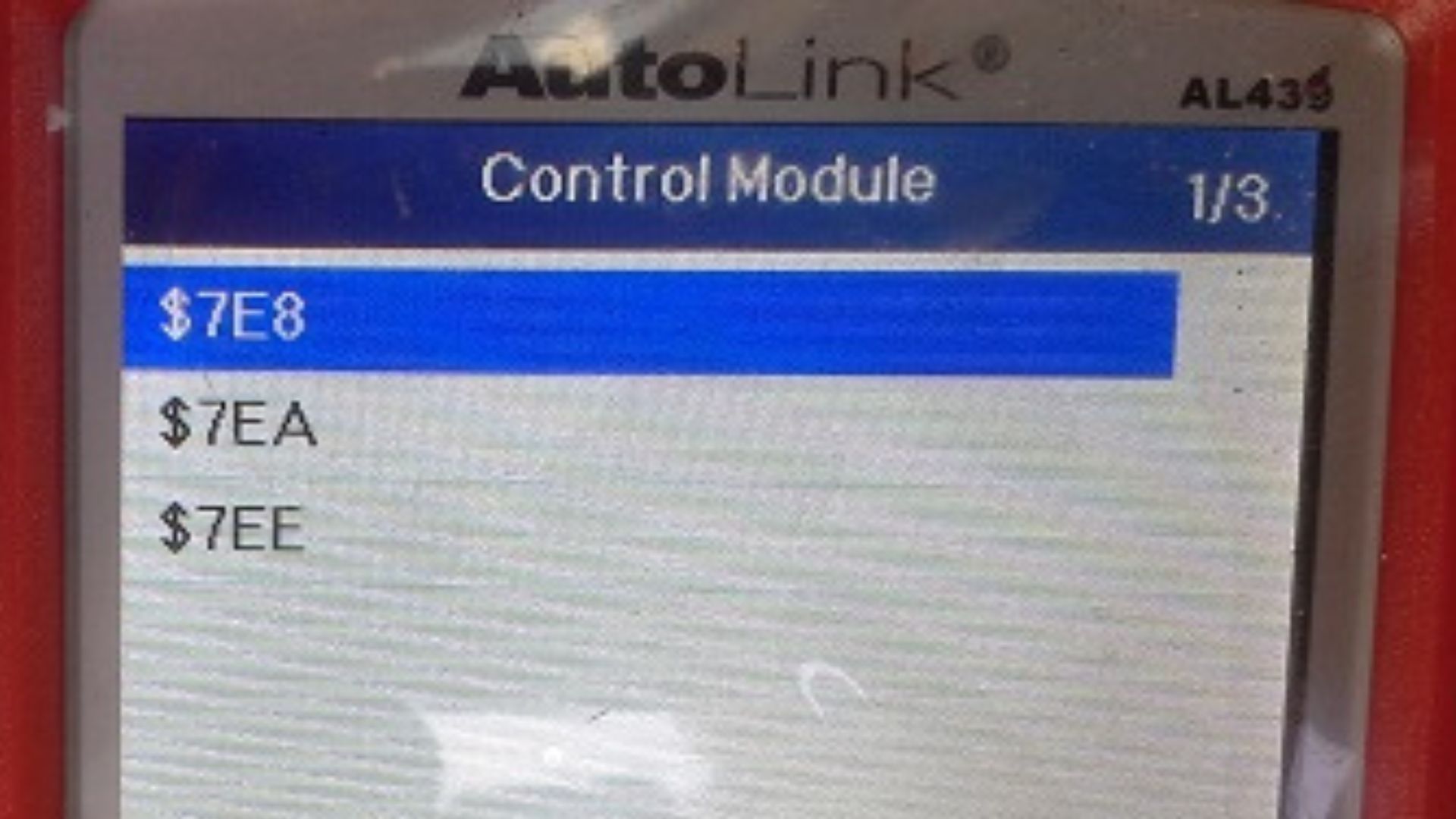
Engine code 7E8
Engine code 7E8 is not an engine code but a submenu for the engine control module. If your OBD scan tool displays engine code 7E8, there is a request code from the engine control module (ECM).

The best way to fix this engine code is by taking your vehicle to the nearest repair shop for service as soon as possible.
Engine code 7E9
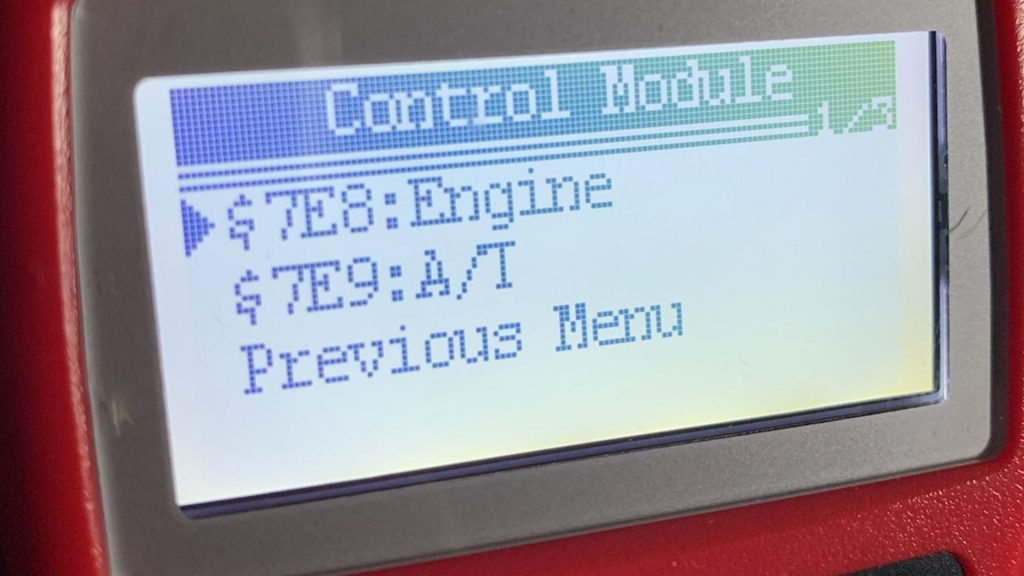
If the OBD scan tool displays 7E9, there is a request code from the transmission control module (TCM). You can fix this engine code by repairing faults or malfunctions in the transmission system.
Engine code 7EA
The OBD scan tool will display this engine code when it needs more information about the engine control unit 3. You can fix this engine code by scanning ECU #3 and fixing faults.
Engine code 7EB
The OBD scan tool will display this code when it needs more information about engine control unit 4. Therefore, you can fix this code by scanning the respective unit for any faults and repairing them.
Is the Engine Code the Same for All Brands?
7E8 and 7E9 are submenus that give you access to fault codes. Even though the submenus are the same for most brands mentioned above, the fault codes may differ from one vehicle to another.
On the other hand, 7EA and 7EB codes are considered Controller Area Network (CAN) identifiers, and they usually indicate which part of the ECU needs scanning. These codes are the same for all brands.
Why does Engine Code Appear?
Damaged oxygen sensor
Your vehicle’s oxygen sensor is responsible for measuring the unburnt oxygen inside the exhaust system. Once the sensor takes the readings, it sends the information to the ECU, which regulates the air and fuel mixture entering the engine cylinders.
Since the oxygen sensor is usually exposed to hot exhaust fumes, it will likely corrode and become damaged quite easily. Even if the oxygen sensor is faulty or damaged, the engine will continue running as usual.
However, you will notice that your vehicle’s fuel economy will start deteriorating. If the oxygen sensor is not replaced in good time, it will damage other crucial engine components such as the catalytic converter and even the spark plugs.
Over time, the engine will misfire, and your vehicle will experience poor acceleration. It is also worth noting that a faulty or damaged oxygen sensor will cause your vehicle to fail emission tests in most parts of the country.
Dirty air/fuel filter
Experts recommend that you should have your engine oil and filter replaced every 5,000 miles. The same also applies to air and fuel filters. These filters ensure that the air and fuel mixture that enters the engine is clean and free from any contaminants or debris. This enables the engine motor to burn fuel properly.
However, if these filters become dirty, your vehicle’s fuel system sensors will send a message to the ECU, which will trigger the engine code to appear.
You can tell these filters are dirty or clogged if the engine starts misfiring, the vehicle becomes difficult to start, or the fuel economy depreciates.
Loose or damaged fuel cap
A loose cap is undoubtedly one of the main reasons the engine code appears. Most modern vehicles have their fuel economy and emissions constantly monitored.
Less pressure will be created inside the fuel cell when the fuel cap is loose, off, or damaged. As a result, the sensors will detect this and send the information to the ECU, which will trigger the engine code to appear.
You can tell you have a damaged fuel cap if it will not lock properly or when your vehicle’s cabin smells like fuel. The best way to fix this problem is to replace the damaged fuel cap with a new one.
Clogged catalytic converter
The catalytic converter fits your vehicle’s exhaust system and converts harmful carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide. During combustion, the catalytic converter filters exhaust fumes before leaving the car through the tailpipe.
Like most filters, the catalytic converter can wear out or become clogged over time, rendering it ineffective. Whenever this happens, an engine error code will appear. A clogged or damaged catalytic converter can cause bad fuel economy, internal engine damage, and even engine misfiring.
Bad spark plug wires and spark plugs
Spark plug wires transfer electricity from the ignition coil to the spark plug. Without a spark plug, the mixture of fuel and air would never ignite. While most vehicles use one spark plug wire per cylinder, others use two spark plug wires for every cylinder.

It is also worth noting that most modern vehicles are not fitted with spark plug wires. Most manufacturers recommend that car owners replace spark plug wires and plugs as part of their regular vehicle maintenance.
If you let the spark plug wires go for long without a replacement, they will go bad, which triggers the engine code to appear. If a spark plug is not replaced in good time, it will cause damage to the catalytic converter and ignition coil.
The most common signs of bad spark plug wires include poor engine performance, bad fuel economy, and rough idle. The good news is that replacing spark plug wires is an easy job without special knowledge or equipment.
Damaged mass air flow sensor
The mass airflow sensor (MAF) is tasked with mixing the correct ratio of air to fuel and ensuring that the mixture burns efficiently inside the combustion chamber.

If the mass air flow is faulty or damaged, the sensor will alert the ECU, and the engine code will appear. The code informs you that it is time to replace or clean the MAF.
A faulty or damaged MAF sensor can make it difficult for your vehicle to start. The best solution to this problem is to have the sensor replaced or cleaned right away.
How to Test an Engine Code?
Once an engine code appears, you need a Bluetooth-compatible OBD scanner to test what the code means, or you can simply take your vehicle to the mechanic to test it for you. If your car is older than 1996, you must purchase an OBD Ⅰ scanner.
On the other hand, if your vehicle was manufactured after 1996, it uses the universal OBD Ⅱ coding system. Therefore, you need to purchase an OBD Ⅱ code reader. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to test an engine code in your vehicle:
- Locate your vehicle’s OBD port
This port is under the driver’s dashboard near the pedals, not far away from the hood release.
The trapezoid-shaped OBD port should be within three feet of the vehicle’s steering wheel and should not require any sophisticated tools to access it. If you have trouble locating the OBD port, you can always refer to your owner’s manual.
- Plug the OBD Ⅱ scan tool into the connector
The scan tool’s end will only fit one way into the connector. Before plugging in the scan tool, ensure the engine and key are off. Once the scan tool has been plugged in, it will immediately power up and communicate with your vehicle’s ECU.
The OBD Ⅱ scanner’s screen may display a message like searching for protocol. However, if the screen does not light up, try jiggling the scan tool to establish better contact.
- Enter your vehicle’s information
Some OBD scanners may request input of your VIN and vehicle’s make/model once you plug them into the connector. They may also ask you about your vehicle’s engine type.
- Read codes in the computer
Once the scanner powers up, you need to locate the menu. Different scanner tools have different operating instructions. Open the main Codes menu and press the scan button to view all the available codes.
- Record the codes that appear
If the scanner displays multiple codes, you need to note them in the same order. Some scan tools may display a description or simply show different letters and numbers. P is the powertrain, B represents the body, C represents the chassis, while U denotes network communications.
- Understand the code meaning and make the necessary repairs or replacement
Every engine error code has its purpose and indicates a specific problem. You can consult a certified professional mechanic if you are having trouble understanding these codes. Once you pinpoint the exact problem, get it repaired.
If a specific component requires a replacement, purchase and install it. Do not wait long before making repairs as it may result in serious problems.
- Erase the code
You can erase the code by plugging the scan tool back into the connector and pressing the erase button. Then, the check engine light will disappear.